Description:
You are given a string, s, and a list of words, words, that are all of the same length. Find all starting indices of substring(s) in s that is a concatenation of each word in words exactly once and without any intervening characters.
For example, given:
You should return the indices: [0,9].
题目理解:
乍一看这是一个字符串匹配问题,但是其实这样想的话就完全错误了,这比字符串匹配问题要复杂多了。
还好的是它所给的单词都是一样长的,这就已经简化了很多的问题,但是它可以给重复的单词,
那么这个问题又不那么简单了,因为这些单词之间可以随意的排列组合,重复的单词会带来很多问题。
那么首先一定要去除重复,不然会对重复的单词进行重复的匹配,并且对排列组合很不利。通常想到的肯定是使用
HashMap来做,这样很快能统计出重复的单词,以及这个单词重复的次数。
因为总长度固定,那么只需要在一个固定长度的窗内去检测是否匹配就好,那么就可以将这个窗从左向右进行滑动,
来一个单词一个单词的匹配。
那么如何进行单词的匹配呢?首先想到的是字符串匹配问题,可以使用KMP 算法来匹配字符串与每一个单词,记录下所有匹配的位置,
注意到每个单词都不同(去除重复之后),单词长度一样,那么它们之间匹配的位置就不会重复。
所有可以直接使用一个与字符串同样长的数组来存储这些下标。
如何查看是否匹配?这时就需要发挥想象力,首先滑动窗是肯定的,在滑动窗中统计很有技巧,这里:
设置一个总距离dis ,表示窗口中单词与字典之间的距离。一个单词的距离就是1 ,所以初始的时候距离为字典的总单词数。
滑动窗口,从字符串上切割 出一个新的单词,如果这个单词与字典中的单词不匹配 ,则不操作。否则匹配 上单词A :
单词A 现在的计数超过 所需个数,距离加一。
单词A 现在的计数不超过 所需个数,距离减一。
滑动窗口,需要将最左端的一个单词弹出 ,进行与上面相反 的操作。
代码一:
注: 这里没有使用HashMap来除去重复。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 public class Solution private int [] matchs; public List<Integer> findSubstring (String s, String[] words) List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if ( s == null || words == null || ( words[0 ].length()*words.length > s.length() ) ) return res; if ( words[0 ].equals("" ) ) { for ( int i = 0 ; i <= s.length() ; i++ ) res.add(i); return res; } char [] ss = s.toCharArray(); matchs = new int [ss.length]; Arrays.fill( matchs, -1 ); int [] counts = new int [words.length]; String[] words_wipe = new String[words.length]; boolean [] used = new boolean [words.length]; int counts_len = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < words.length; i++ ) { if ( !used[i] ) { words_wipe[counts_len] = words[i]; counts[counts_len] = 1 ; for ( int j = i + 1 ; j < words.length; j++ ) { if ( words[i].equals(words[j]) ) { counts[counts_len]++; used[j] = true ; } } counts_len++; } } for ( int i = 0 ; i < counts_len; i++ ) { KMP(ss, words_wipe[i].toCharArray(), i); } int step = words_wipe[0 ].length(), dis = words.length, total_len = dis * step; int [] sub_count = new int [counts_len]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < step; i++ ) { Arrays.fill(sub_count, 0 ); dis = words.length; for ( int j = i; j < ss.length; j += step ) { int head = j - total_len; if ( head > -1 && matchs[head] != -1 ) { dis = sub_count[matchs[head]] <= counts[matchs[head]] ? dis + 1 : dis - 1 ; sub_count[matchs[head]]--; } if ( matchs[j] == -1 ) continue ; dis = sub_count[matchs[j]] >= counts[matchs[j]] ? dis + 1 : dis - 1 ; sub_count[matchs[j]]++; if ( dis == 0 ) res.add(j - total_len + step); } } return res; } private void KMP (char [] t, char [] p, int widx) int [] pai = computePai(p); int match_idx = -1 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < t.length; i++ ) { while ( match_idx > -1 && p[match_idx + 1 ] != t[i] ) match_idx = pai[match_idx]; if ( p[match_idx + 1 ] == t[i] ) match_idx++; if ( match_idx == p.length - 1 ) { matchs[i - p.length + 1 ] = widx; match_idx = pai[match_idx]; } } } private int [] computePai(char [] p) { int [] pai = new int [p.length]; pai[0 ] = -1 ; int k = -1 ; for ( int idx = 1 ; idx < p.length; idx++ ) { while ( k > -1 && p[k+1 ] != p[idx] ) k = pai[k]; if ( p[k+1 ] == p[idx] ) k = k + 1 ; pai[idx] = k; } return pai; } }
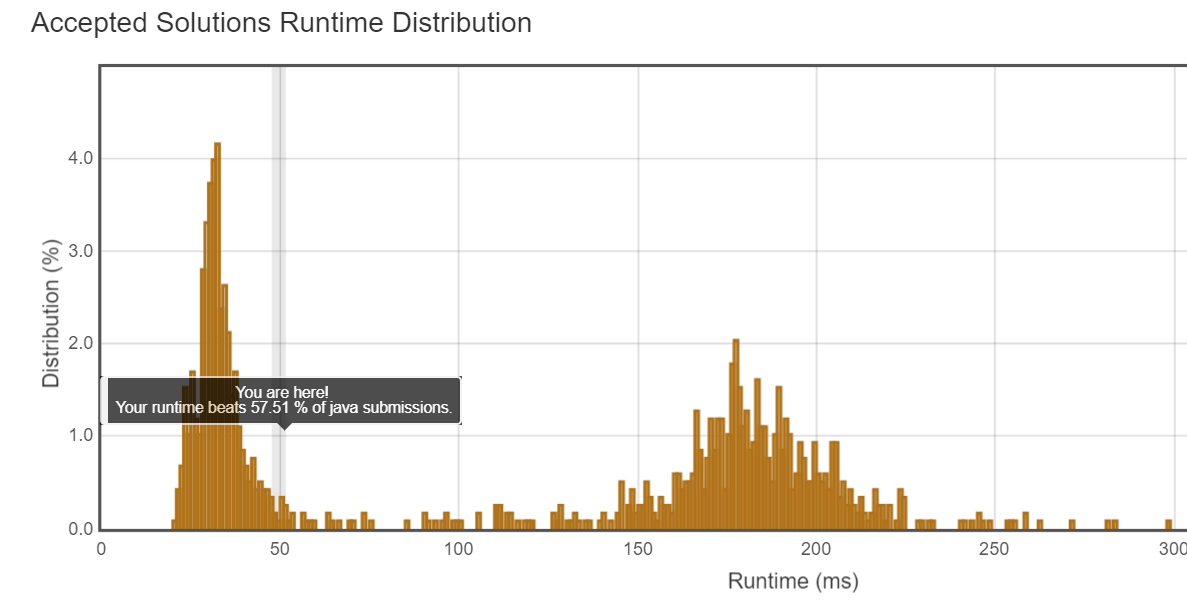
复杂度:O(mn)?
代码还是很垃圾,所以和别人的差距在哪里,实在是想不出来,查看别人代码后发现,别人使用的是HashMap的Hash 功能来匹配单词的,
这样通过Hash 来进行两个个单词的匹配,复杂度是O(1) ,额,原来Hash 是这样使用的…
另外这里还要翻转一下思维,上面是用单词去匹配字符串,这里由于先建好了一个单词的HashMap,所以直接将字符串切割,
然后使用切出的单词使用HashMap查询就能知道它的次数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class Solution public List<Integer> findSubstring (String s, String[] words) List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); int m = s.length(), n = words.length, step = words[0 ].length(), bound = m - step, total_len = step * n; Map< String, Integer> words_list = new HashMap<>(n); int [][] counts = new int [2 ][n]; Integer index = 0 , temp; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++ ) { if ( ( temp = words_list.get(words[i])) != null ) counts[0 ][temp]++; else { words_list.put( words[i], index); counts[0 ][index++] = 1 ; } } int [] matchs = new int [bound + 1 ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i <= bound; i++ ) { String s_sub = s.substring(i, i + step); matchs[i] = ((temp = words_list.get(s_sub)) != null ) ? temp : -1 ; } for ( int i = 0 ; i < step; i++ ) { Arrays.fill(counts[1 ], 0 ); int dis = n; for ( int j = i; j <= bound; j += step ) { int head = j - total_len; if ( head > -1 && matchs[head] != -1 ) { dis = counts[1 ][matchs[head]] <= counts[0 ][matchs[head]] ? dis + 1 : dis - 1 ; counts[1 ][matchs[head]]--; } if ( matchs[j] == -1 ) continue ; dis = counts[1 ][matchs[j]] >= counts[0 ][matchs[j]] ? dis + 1 : dis - 1 ; counts[1 ][matchs[j]]++; if ( dis == 0 ) res.add(j - total_len + step); } } return res; } }
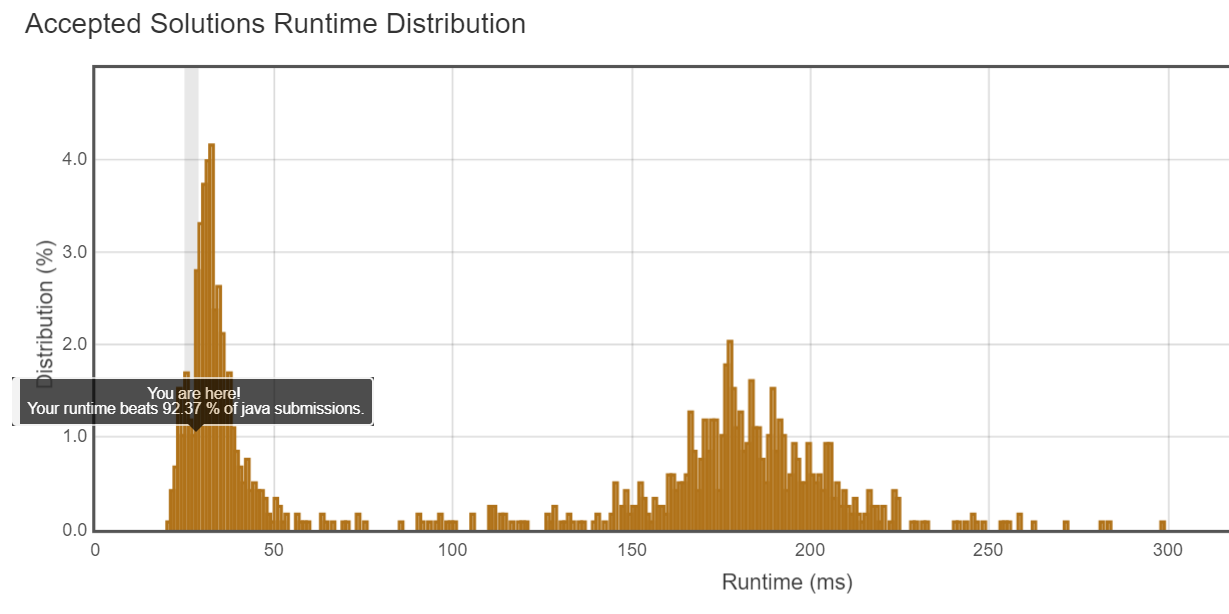
复杂度:O(n)。