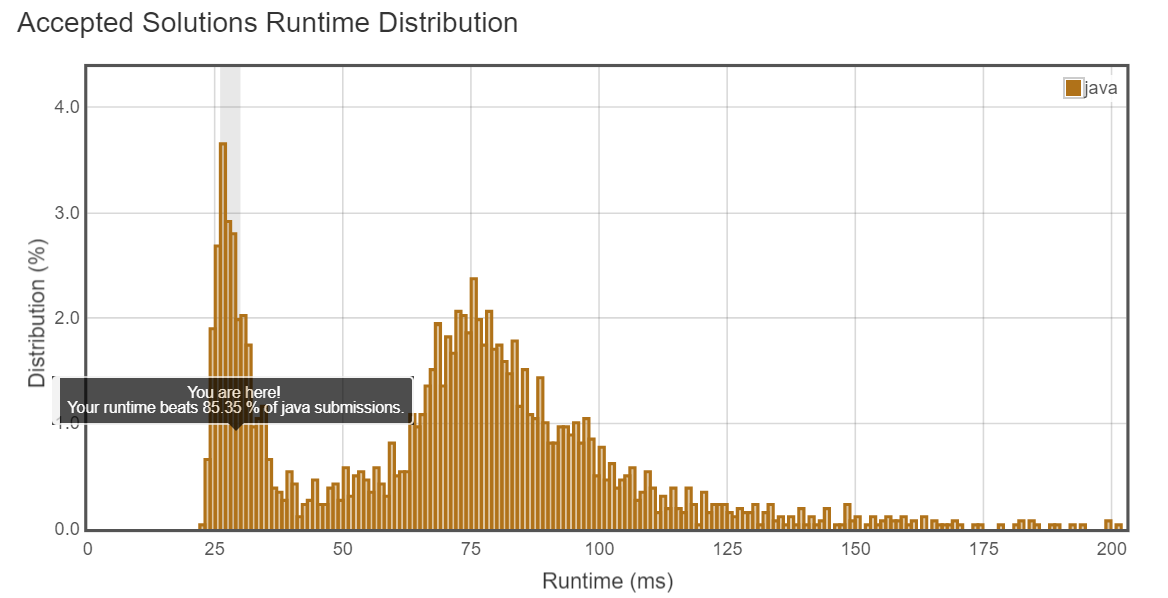
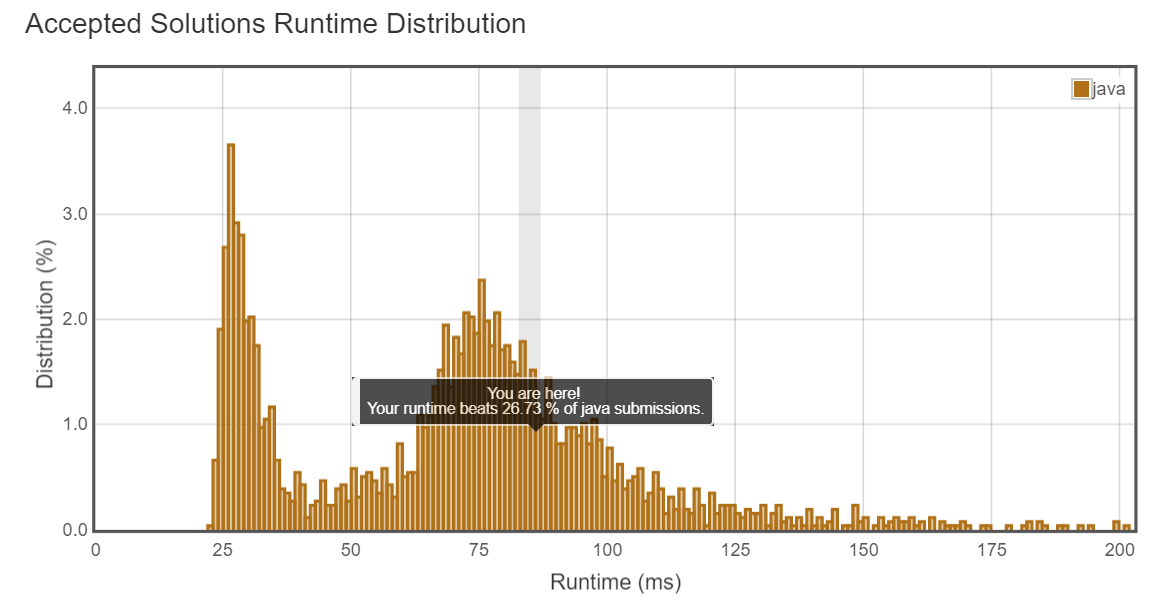
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
| public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if ( nums.length < 4 ) return result;
Arrays.sort(nums);
int[] ynums = new int[nums.length];
int repeat = 1, idx = 1;
ynums[0] = nums[0];
for ( int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++ ) {
if ( nums[i] == nums[i-1] ) {
repeat++;
} else {
repeat = 1;
}
if ( repeat < 4 ) {
ynums[idx++] = nums[i];
} else if ( repeat == 4 && nums[i]*4 == target ) {
myAdd( result, nums[i], nums[i], nums[i], nums[i]);
}
}
int m = idx, ts_i = 0;
int[][] two_sum = new int[m*(m-1)/2][3];
for ( int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++ ) {
repeat = 1;
while ( i < m - 1 && ynums[i + 1] == ynums[i] ) {
i++;
repeat++;
}
if ( repeat == 2 ) {
two_sum[ts_i][0] = ynums[i] * 2;
two_sum[ts_i][1] = i - 1;
two_sum[ts_i][2] = i;
ts_i++;
} else if ( repeat == 3 ) {
two_sum[ts_i][0] = ynums[i] * 2;
two_sum[ts_i][1] = i - 1;
two_sum[ts_i][2] = i - 1;
ts_i++;
}
for ( int j = i + 1; j < m; ) {
two_sum[ts_i][0] = ynums[i] + ynums[j];
two_sum[ts_i][1] = i;
two_sum[ts_i][2] = j;
ts_i++;
j++;
while ( j < m && ynums[j] == ynums[j-1] ) {
j++;
}
}
}
Arrays.sort(two_sum, 0, ts_i, new MyCompare());
int l = 0, r = ts_i - 1;
while ( l < r ) {
int sum = two_sum[l][0] + two_sum[r][0];
if ( sum < target ) {
l++;
} else if ( sum > target ) {
r--;
} else {
if ( two_sum[l][2] < two_sum[r][1] ) {
myAdd( result, ynums[two_sum[l][1]], ynums[two_sum[l][2]], ynums[two_sum[r][1]], ynums[two_sum[r][2]]);
}
int ll = l + 1, rr = r - 1;
while ( ll < r && two_sum[ll][0] == two_sum[ll-1][0] ) {
if ( two_sum[ll][2] < two_sum[r][1] ) {
myAdd( result, ynums[two_sum[ll][1]], ynums[two_sum[ll][2]], ynums[two_sum[r][1]], ynums[two_sum[r][2]]);
}
ll++;
}
while ( ll < rr && two_sum[rr][0] == two_sum[rr+1][0] ) {
if ( two_sum[rr][1] > two_sum[l][2] ) {
myAdd( result, ynums[two_sum[l][1]], ynums[two_sum[l][2]], ynums[two_sum[rr][1]], ynums[two_sum[rr][2]]);
}
rr--;
}
l++; r--;
}
}
return result;
}
private void myAdd( List<List<Integer>> result, int a1, int a2, int b1, int b2) {
List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>();
item.add(a1); item.add(a2);
item.add(b1); item.add(b2);
result.add(item);
}
private class MyCompare implements Comparator<int[]> {
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
if ( o1[0] > o2[0] ) {
return 1;
} else if ( o1[0] < o2[0] ) {
return -1;
} else {
if ( o1[1] < o2[1] ) {
return -1;
} else if ( o1[1] > o2[1] ) {
return 1;
} else {
if ( o1[2] < o2[2] ) {
return -1;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
|